AI Generator for
Quizzes, Flashcards
& More
Transform your boring study content into interactive AI-powered worksheets, quizzes, flashcards, and practice questions with a click of a button. Upload PDFs, documents, audio and video today to get started.
Stop the manual work
Most students waste time on inefficient learning methods
Instead of re-reading your long documents or manually creating flashcards and summaries for hours, we help you skip these steps.
Stop drowning in information and let our AI filter out what’s really important. Quickly start testing yourself and improve faster.
Very few people can afford a personal tutor. StudyBlaze changes this forever. Interactive learning makes your progress 10x faster.
Manually creating study materials is time that you could spend training and testing yourself. Reduce stress by eliminating manual work entirely.
An AI Tutor available 24/7
Have access to a tutor everyday
Receive instant feedback on your answers
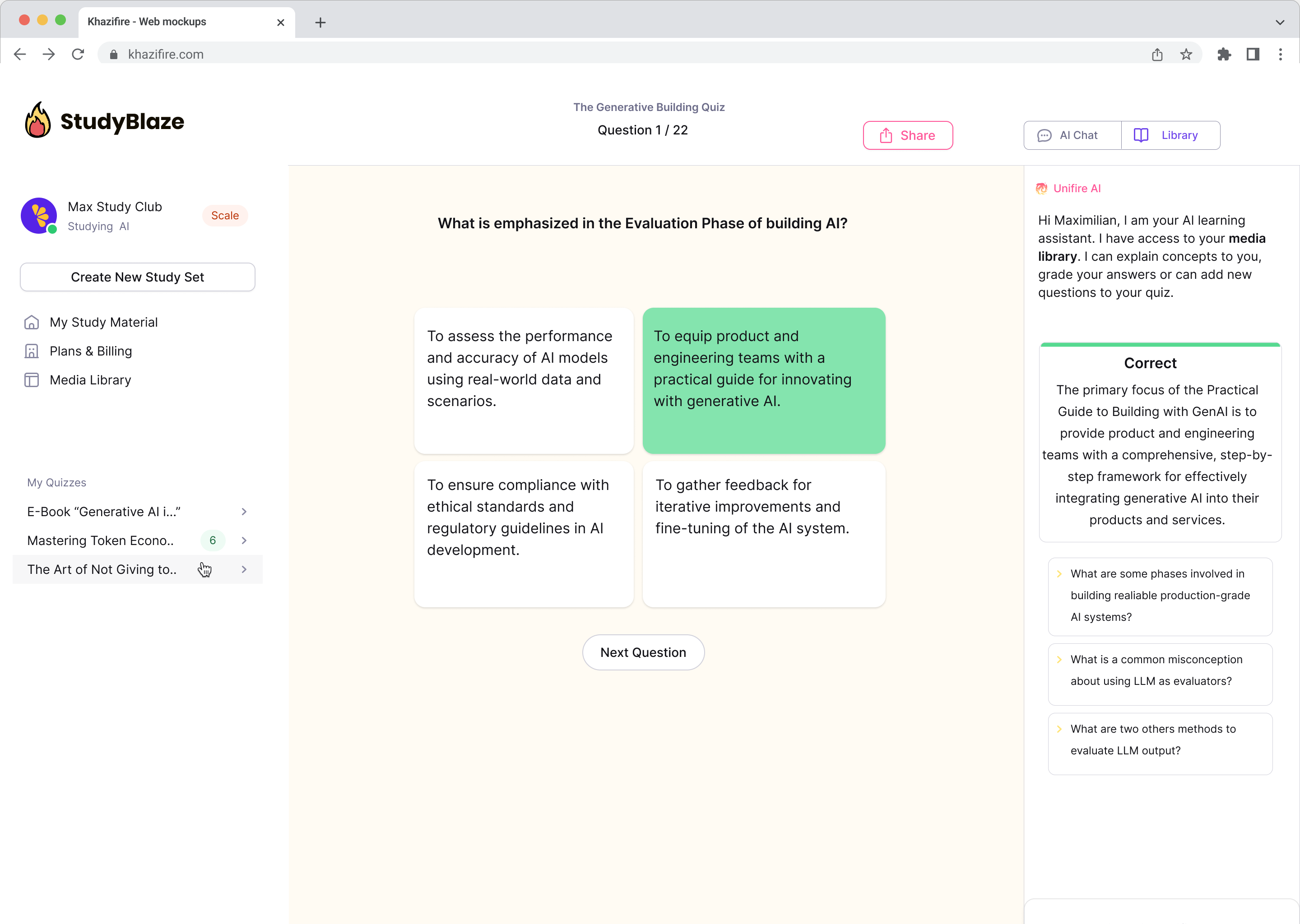
Chat with your documents and understand complex topics quicker
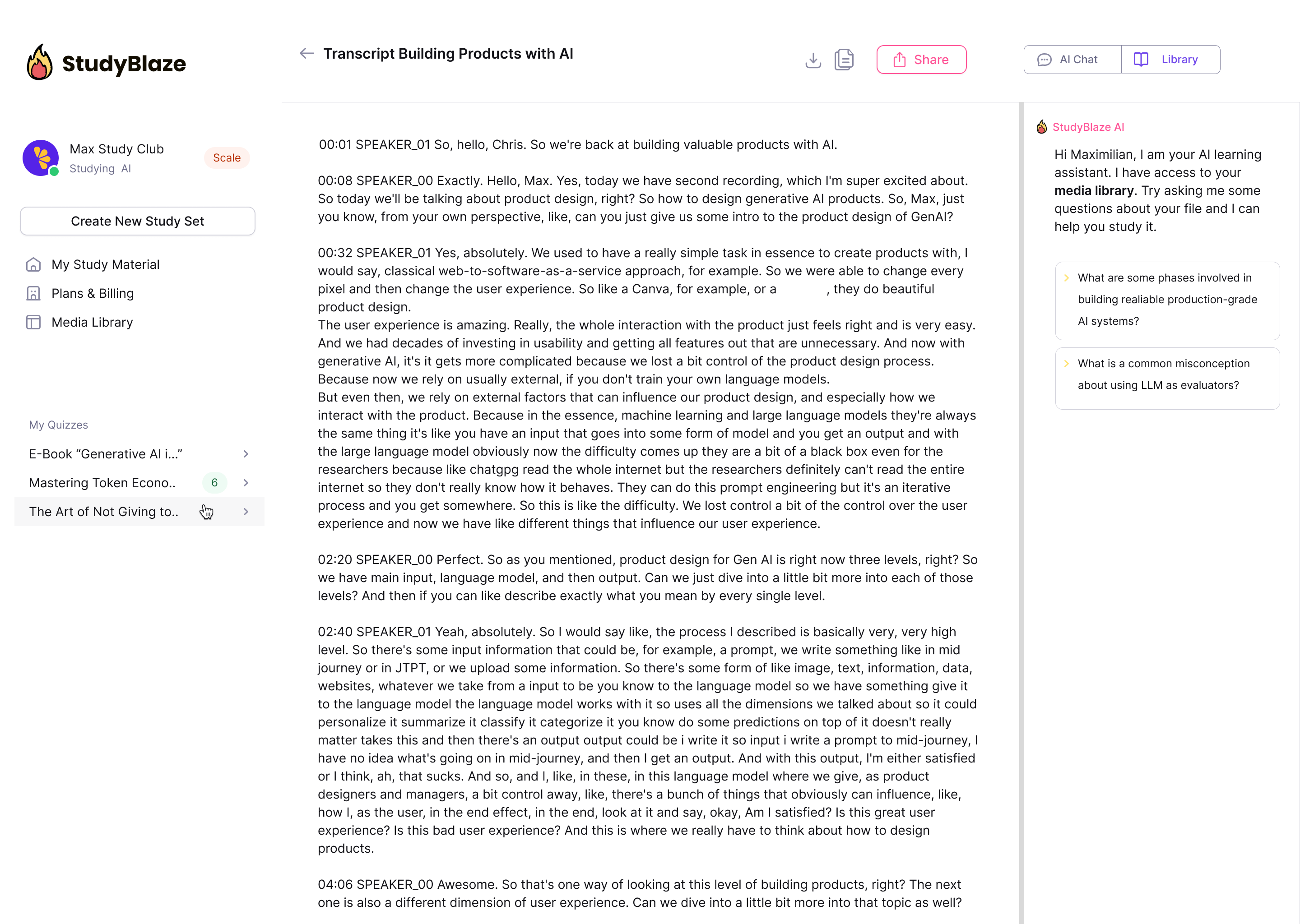
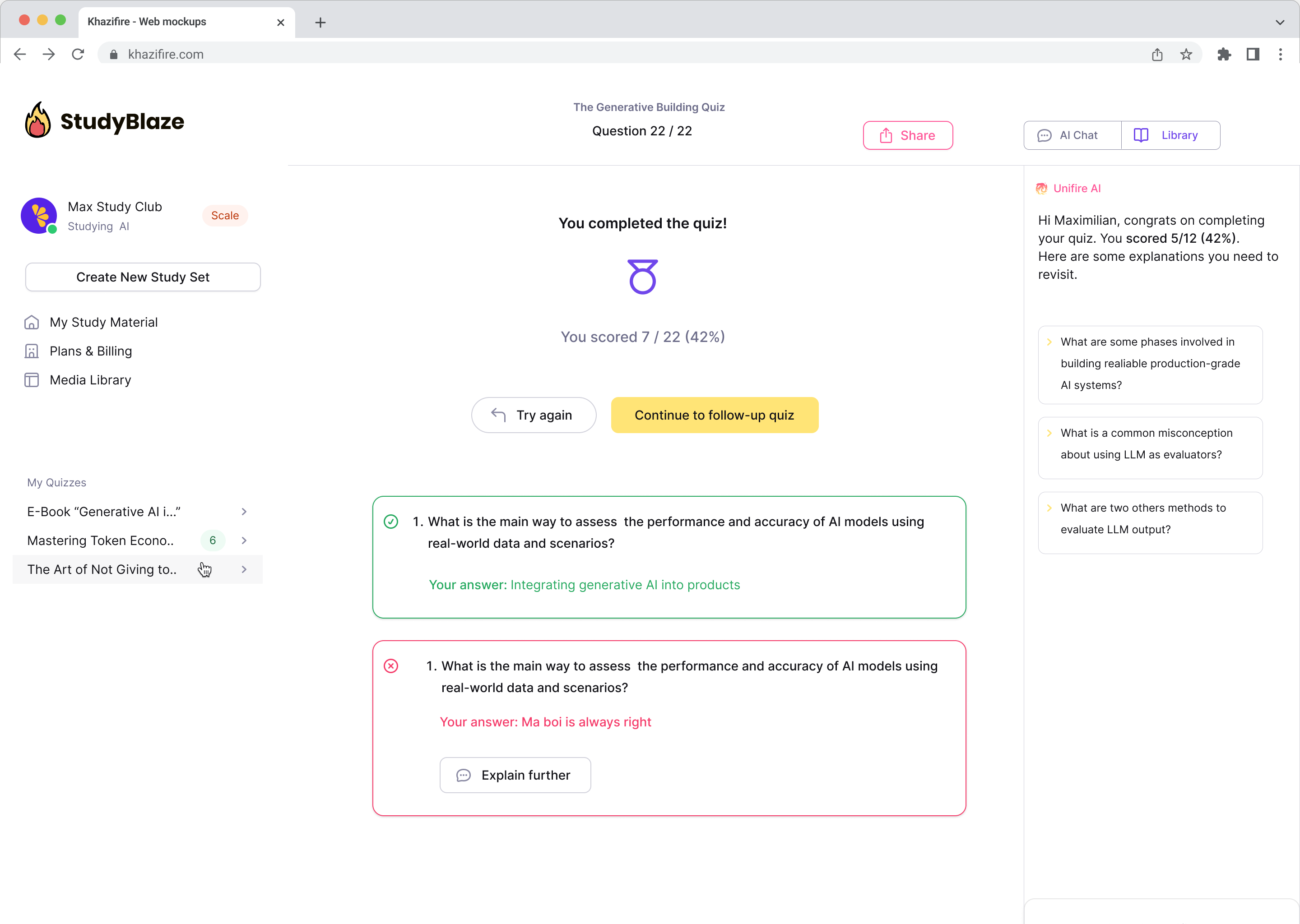
Let your AI tutor grade your answers and tell you what you missed
Most popular questions
We answer the most important questions users like you have.
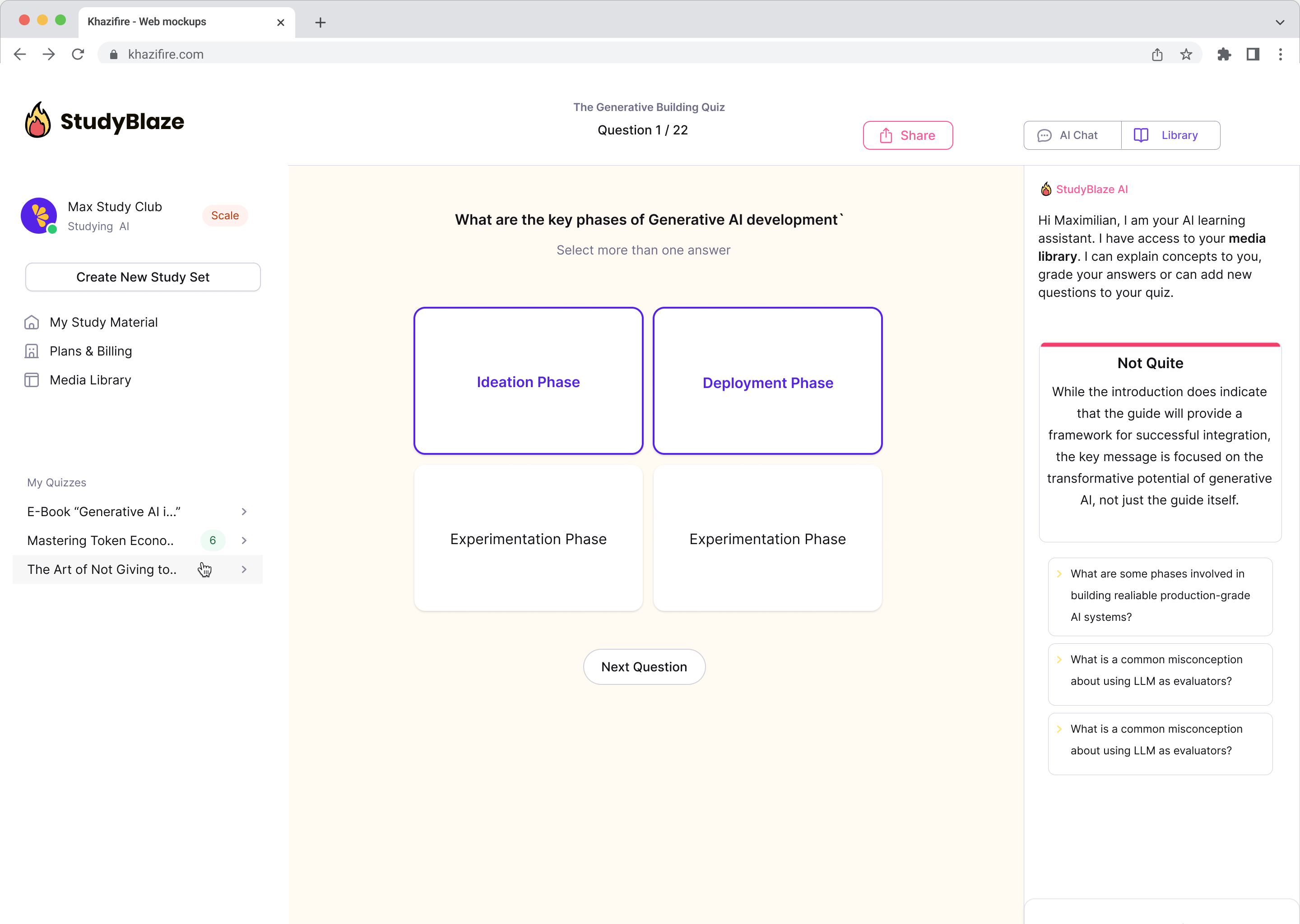
Upgrade your studying habits
With StudyBlaze you can immediately improve your learning speed. Instead of reading boring materials over and over again, get to test your knowledge faster without hours of manual flashcard and summary creation.
